Este articulo necesita una revisión editorial. Cómo puedes ayudar.
Esta traducción está incompleta. Por favor, ayuda a traducir este artículo del inglés.
CSS3 es la última evolución del lenguaje de las Hojas de Estilo en Cascada (Cascading Style Sheets), y pretende ampliar la versión CSS2.1. Trae consigo muchas novedades altamente esperadas , como las esquinas redondeadas, sombras, gradientes , transiciones o animaciones, y nuevos layouts como multi-columnas, cajas flexibles o maquetas de diseño en cuadrícula (grid layouts).
Las partes experimentales son particulares para cada navegador y deberían ser evitadas en entornos de producción, o usadas con extrema precaución, ya que tanto la sintaxis como la semántica pueden cambiar en el futuro.
Los módulos y el proceso de estandarización
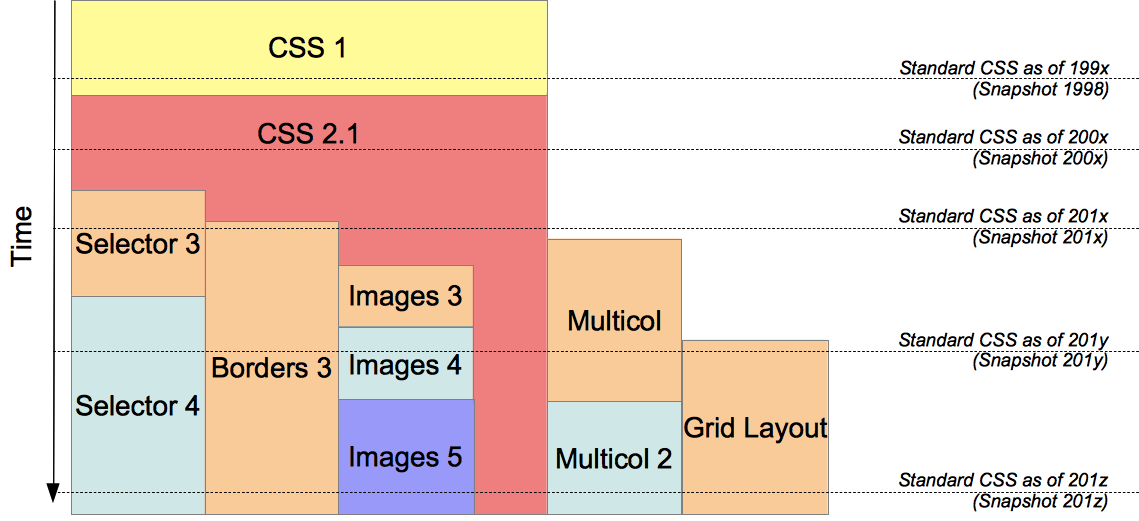
El Nivel 2 de CSS necesitó 9 años, desde Agosto de 2002 hasta Junio de 2011, para alcanzar el estado de Recomendación. Esto fué debido al hecho de que algunas características secundarias fueron retiradas de las especificaciones globales, con el fin de acelerar la normalización de las características no problemáticas, el Grupo de Trabajo CSS de la W3C, en una decisión referida como la doctrina Beijing dividió CSS en componentes más pequeños llamados módulos cada uno de estos módulos es ahora una parte independiente del lenguaje y se dirije a la estandarización a su propio ritmo mientras algunos módulos son ya recomendados de la W3C, otros todavía son borradores iniciales tambíen se añaden nuevos módulos cuando se identifican nuevas necesidades.
Formalmente, no existe un estandar de CSS3 por sí solo cada módulo es estandarizado independientemente, por lo que el estandar CSS consiste en CSS2.1 modificado y extendido por módulos terminados, no necesariamente todos con el mismo nivel numérico por tanto, puede ser definido un panorama del CSS estandar listando (enumerando) CSS2.1 y los módulos maduros.
El consorcio W3 publica periodicamente ciertos snapshots(imágenes), como en 2007 o 2010.
Aunque hoy en día ningún módulo con nivel mayor al 3 es estandarizado, esto cambiará en el futuro. Algunos módulos, como Selectors 4 o CSS Borders y Backgrounds nivel 4 tienen ya un borrador de edición pese a que aún no tienen un estatus de primer borrador de trabajo.
Estado de los módulos CSS
Módulos estables
Unos pocos módulos CSS son lo suficientemente estables y han alcanzado uno de los tres niveles de recomendación de CSSWG: Candidato (Candidate), Recomendación (Recommendation), Recomendación propuesta o Recomendación (Proposed Recommendation or Recommendation). Estos puden ser usados sin un prefijo y son muy estables aunque algunas características aun pueden ser eliminadas de la etapa de Candidate Recommendation.
Estos módulos extienden y mejoran la especificación CSS2.1 la cual construye el núcleo de la especificación. Juntos, son el snapshot actual de la especificación CSS.
| CSS Color Module Level 3 | Recommendation desde el 7 de Junio de 2011 |
|
Agrega la propiedad Ahora el color transparente es un color real (gracias al soporte para el canal alpha) y es un alias para Deja obsoleto las keyworks del sistema de colores (system-color) las cuales ya no deberían ser usadas en ambientes de producción. |
|
| Selectors Level 3 | Recommendation desde el 29 de Septiembre de 2011 |
|
Agrega:
|
|
La siguiente iteración de la especificación de Selectores ya está en progreso, aunque aún no ha alcanzado el estado de primer borrador público de trabajo.
| CSS Namespaces Module | Recommendation desde el 29 de Septiembre de 2011 |
|
Añade soporte para los nombres de espacio XML (namespaces) definiendo la noción de nombre CSS cualificado (CSS qualified name), usando la sintaxis ' | ' y agregando la regla CSS |
|
| Media Queries | Recommendation desde el 19 de Junio de 2012 |
|
Extiende los tipos anteriores de media ( Los Media queries no sólo son usado en documentos CSS sino también en algunos atributos de elementos HTML, como el atributo |
|
La siguiente generación de esta especificación está en progreso, permitiendo adaptar un sitio Web con respecto a los métodos de entrada disponibles en el agente del usuario con las nuevas características media como hover o pointer. También está propuesta la detección de soporte EcmaScript usando media script.
| CSS Style Attributes | Recommendation desde el 7 de Noviembre de 2013 |
|
Define formalmente la sintaxis del contenido del atributo global |
|
| CSS Backgrounds and Borders Module Level 3 | Candidate Recommendation |
|
Agrega:
|
|
El CSS4 Iteración de fondos y Especificación de bordes ya está en progreso; aunque aún no ha alcanzado el estado del Primer Borrador de Trabajo Público, este planea agregar la característica de acortar los bordes (en el CSS border-clip, border-clip-top, border-clip-right, border-clip-bottom, y border-clip-left propiedades) o controlar la forma del borde en una esquina (usandopropiedad CSS border-corner-shape).
| CSS Multi-column Layout Module | Candidate Recommendation |
Se agrega soporte para el diseño fácil de multi-columnas usando CSS columns, column-count, column-fill, column-gap, column-rule, column-rule-color, column-rule-style, column-rule-width, column-span, column-width, break-after, break-before, and break-inside. |
|
| CSS Speech Module | Candidate Recommendation |
Defines the speech media type, an aural formatting model and numerous properties specific for speech-rendering user agents. |
|
| CSS Image Values and Replaced Content Module Level 3 | Candidate Recommendation |
|
Se define el tipo de dato Se extiende la sintaxis de Agregados:
|
|
The CSS Image Values and Replaced Content Level 4 which will supersede CSS Image Level 3 is in development and is a Working Draft.
| CSS Values and Units Module Level 3 | Candidate Recommendation |
|
Makes Formally defines the CSS data types of CSS 2.1, that were implicitely defined by their grammar token and some textual precisions. Adds:
|
|
Several types definition, like <ident> and <custom-ident>, have been deferred to CSS Values and Units Module Level 4.
| CSS Flexible Box Layout Module | Candidate Recommendation |
Add a flexbox layout to the CSS display property and several new CSS properties to control it: flex, flex-align, flex-direction, flex-flow, flex-item-align, flex-line-pack, flex-order, flex-pack, and flex-wrap. |
|
| CSS Conditional Rules Module Level 3 | Candidate Recommendation |
Adds features for conditional processing of parts of style sheets, conditioned on capabilities of the browser or the document the style sheet is being applied to. It consists mainly in allowing nested at-rules inside @media and the adding of a new CSS at-rule, @supports, and a new DOM method CSS.supports(). |
|
| Unknown | Unknown |
|
Extends:
Adds:
Precises:
At risk: due to insufficient browser support, standardization of the |
|
| CSS Fonts Module Level 3 | Candidate Recommendation |
|
Amends the CSS2.1 Font matching algorithm to be closer to what is really implemented. Adds:
|
|
| CSS Syntax Level 3 | Candidate Recommendation |
| Precises how charsets are determined; minor changes in parsing and tokenization algorithms. | |
Modules in the refining phase
Specifications that are deemed to be in the refining phase are already fairly stable. Though changes are still expected, they shouldn't create incompatibilities with current implementations; they should mainly define behavior in edge cases.
| CSS Basic User Interface Module Level 3 | Candidate Recommendation |
|
Adds:
|
|
An early list of what could be in the next iteration of the CSS Basic User Interface Module is available.
| CSS Transitions | Working Draft |
Allows the definition of transitions effects between two properties values by adding the CSS transition, transition-delay, transition-duration, transition-property, and transition-timing-function properties. |
|
| CSS Animations | Working Draft |
Allows the definition of animations effects by adding the CSS animation, animation-delay,animation-direction, animation-duration, animation-fill-mode, animation-iteration-count, animation-name, animation-play-state, and animation-timing-function properties, as well as the @keyframes at-rule. |
|
| CSS Transforms Level 1 | Working Draft |
|
Adds:
Note: this specification is a merge of CSS 2D-Transforms, CSS 3D-Transforms and SVG transforms. |
|
| CSS Fragmentation Module Level 3 | Candidate Recommendation |
| Defines how partitions of a Web page should happen, that is page, column breaks, and widows and orphans handling.
Adds:
|
|
| CSS Text Level 3 | Working Draft |
|
Extends:
Adds:
|
|
A few features present in early CSS Text Level 3 draft have being postponed to the next iteration of this module .
| CSS Custom Properties for Cascading Variables Module Level 1 | Working Draft |
| Defines a mechanism allowing to define variables in CSS. | |
Modules in the revising phase
Modules that are in the revising phase are much less stable than those in the refining phase. Often the syntax is still under scrutiny and may evolve a lot, in a non-compatible way. Alternative syntax are tested and often implemented.
| CSS Writing Modes Module Level 3 | Candidate Recommendation |
Defines the writing modes of both horizontal and vertical scripts and precises how the CSS direction and unicode-bidi properties interact with the new CSS text-orientation property, and extends them where needed. |
|
Modules in the exploring phase
| CSS Image Values and Replaced Content Module Level 4 | Working Draft |
|
Extends:
Adds:
|
|
| CSS Device Adaptation | Working Draft |
Adds a new at-rule, @viewport, allowing to specify the size, zoom factor, and orientation of the viewport that is used as the base for the initial containing block. |
|
| CSS Grid Layout | Working Draft |
Add a grid layout to the CSS display property and several new CSS properties to control it: grid, grid-area, grid-auto-columns, grid-auto-flow, grid-auto-position, grid-auto-rows, grid-column, grid-column-start, grid-column-end, grid-row, grid-row-start, grid-row-end, grid-template, grid-template-areas, grid-template-rows, and grid-template-columns. |
|
| CSS Generated Content for Paged Media Module | Working Draft |
| Adds the ability to tailor printed version of a document by allowing to control header, footer but also references tables like indexes or tables of content. | |
| Unknown | Unknown |
| Extends the floats mechanism to define exclusion regions in any positioning scheme. Adds the notion of shapes, in which content must flows. | |
| CSS Lists and Counters Module Level 3 | Working Draft |
| Extends the list counter mechanism so that list markers can be styled and Web developers can define new list counter schemes. | |
| CSS Regions Module Level 1 | Working Draft |
| Defines a new mechanism allowing content to flow across, eventually non-contiguous, multiple areas called regions. | |
| CSS Device Adaptation | Working Draft |
Adds a new at-rule, @viewport, allowing to specify the size, zoom factor, and orientation of the viewport that is used as the base for the initial containing block. |
|
| Filter Effects Module Level 1 | Working Draft |
| CSS Grid Layout | Working Draft |
| CSS Intrinsic & Extrinsic Sizing Module Level 3 | Working Draft |
| CSS Line Grid Module Level 1 | Working Draft |
| CSS Positioned Layout Module Level 3 | Working Draft |
| CSS Ruby Layout Module Level 1 | Working Draft |
| CSS Object Model (CSSOM) | Working Draft |
| CSS Overflow Module Level 3 | Working Draft |
| CSS Font Loading Module Level 3 | Working Draft |
| CSS Display Module Level 3 | Working Draft |
| CSS Scoping Module Level 1 | Working Draft |
| Media Queries Level 4 | Working Draft |
| Non-element Selectors Module Level 1 | Working Draft |
| Geometry Interfaces Module Level 1 | Candidate Recommendation |
| CSS Inline Layout | Working Draft |
Modules in the rewriting phase
Modules that are in the rewriting phase are outdated and require to be rewritten. The syntax is still under scrutiny and may evolve a lot, in a non-compatible way. Alternative syntaxes are tested and often implemented.
| CSS Basic Box Model | Working Draft |
| CSS Generated Content Module Level 3 | Working Draft |
| Unknown | Unknown |