Diese Übersetzung ist unvollständig. Bitte helfen Sie, diesen Artikel aus dem Englischen zu übersetzen.
Wenn ein Benutzer eine Seite betrachtet, die über HTTPS bereit gestellt wird, ist die Verbindung mit TLS verschlüsselt und deshalb geschützt gegen Sniffer und
Man-in-the-Middle-Angriffe.
Wenn die HTTPS- Seite Inhalte enthält, die über reguläres Klartext HTML abgerufen werden, ist die Verbindung nur teilweise verschlüsselt: Der unverschlüsselte Inhalt ist zugänglich für Sniffer und kann durch Man-in-the-Middle-Angriffe verändert werden, weshalb die Verbindung nicht mehr geschützt ist. Eine Website, die dieses Verhalten aufweist, wird als Mixed Content-Seite bezeichnet.
Webkonsole
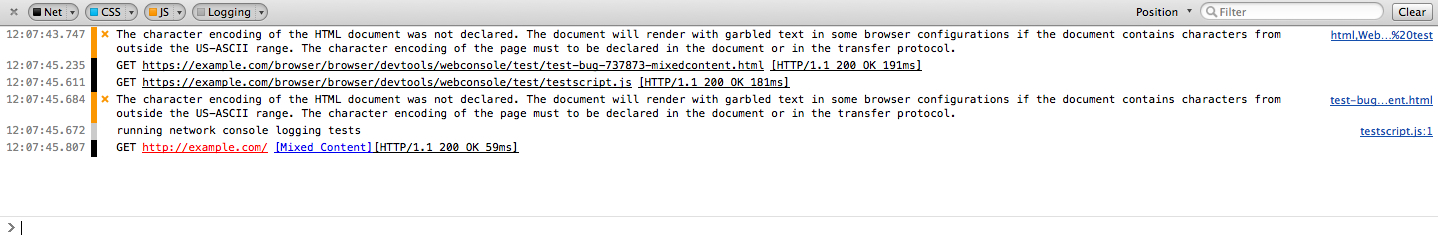
Wird Firefox 16 gestartet, so erscheint auf der Webkonsole ein Mixed Content- Warnhinweis. Die über HTML geladene Mixed Content- Ressource wird in Rot angezeigt, zusammen mit dem Text "mixed content" , der ein Link zu dieser Seite ist.
Um diesen Fehler zu beseitigen, sollten HTTP- Inhalte entfernt und durch solche ersetzt werden, die über HTTPS bereitgestellt werden. Häufige Beispiele für Mixed Content enthalten JavaScript- Dateien, Stylesheets, Bilder, Videos und andere Medien.
Wenn Firefox 23 gestartet wird, ist aktiver Mixed Content in der Standardeinstellung geblockt (und angezeigter Mixed Content kann optional geblockt werden). Um es für Web-Entwickler einfacher zu machen, Mixed Content- Fehler zu finden, sind alle geblockten Mixed Content- Anfragen im Sicherheitsfenster der Webkonsole aufgeführt.
Types of Mixed Content
There are two categories for mixed content: Mixed Passive/Display Content and Mixed Active Content. The difference lies in the threat level of the worst case scenario if content is rewritten as part of a Man-In-The-Middle attack. In the case of passive content, the threat is low (webpage appears broken or with misleading content). In the case of active content, the threat can lead to phishing, sensitive data disclosure, redirection to malicious sites, etc.
Mixed passive/display content
Mixed Passive/Display Content is content served over HTTP that is included in an HTTPS webpage, but that cannot alter other portions of the webpage. For example, an attacker could replace an image served over HTTP with an inappropriate image or message to the user. The attacker could also infer information about the user's activities by watching which images are served to the user; often images are only served on a specific page within a website. If the attacker observes HTTP requests to certain images, he could determine which webpage the user is visiting.
Passive content list
This section lists all types of HTTP requests which are considered passive content:
- <audio> (
srcattribute) - <img> (
srcattribute) - <video> (
srcattribute) - <object> subresources (when an <object> performs HTTP requests)
Mixed active content
Mixed Active Content is content that has access to all or parts of the Document Object Model of the HTTPS page. This type of mixed content can alter the behavior of the HTTPS page and potentially steal sensitive data from the user. Hence, in addition to the risks described for Mixed Display Content above, Mixed Active Content is vulnerable to a few other attack vectors.
In the Mixed Active Content case, a man-in-the-middle attacker can intercept the request for the HTTP content. The attacker can also rewrite the response to include malicious JavaScript code. Malicious active content can steal the user's credentials, acquire sensitive data about the user, or attempt to install malware on the user's system (by leveraging vulnerabilities in the browser or its plugins, for example).
The risk involved with mixed content does depend on the type of website the user is visiting and how sensitive the data exposed to that site may be. The webpage may have public data visible to the world or private data visible only when authenticated. If the webpage is public and has no sensitive data about the user, using Mixed Active Content still provides the attacker with the opportunity to redirect the user to other HTTP pages and steal HTTP cookies from those sites.
Active content list
This section lists some types of HTTP requests which are considered active content:
- <script> (
srcattribute) - <link> (
hrefattribute) (this includes CSS stylesheets) - XMLHttpRequest object requests
- <iframe> (
srcattributes) - All cases in CSS where a url value is used (@font-face, cursor, background-image, etc.)
- <object> (
dataattribute)
See also