« CSS « CSS z-index 이해하기
쌓임 맥락 예제2
굉장히 간단하지만 쌓임 맥락을 이해하는데 도움이 되는 예제를 하나 소개하려 한다. 이전 예제에서 본 4개의 DIV가 있다. 이번에는 두 레벨의 DIV 모두 z-index 속성 값을 지정했다.
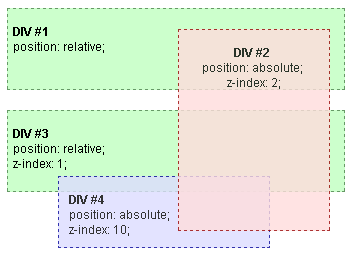
z-index 속성 값이 2인 DIV #2는 z-index 속성 값이 1인 DIV #3 위에 있다. 왜냐하면 DIV #2와 DIV #3은 같은 쌓임 맥락(루트 엘리먼트)에 속하고 DIV #2의 z-index 값이 더 크기 때문이다.
이상한 점은 z-index 속성 값이 2인 DIV #2가 z-index 속성 값이 10인 DIV #4보다 위에 있다는 점이다. 이것은 이 두 DIV가 같은 쌓임 맥락에 속해있지 않기 때문이다. DIV #4는 DIV #3이 만든 쌓임 맥락에 속해있고 DIV #3과 DIV #3의 모든 자식 엘리먼트는 DIV #2보다 아래에 있다.
이 상황을 더 잘 이해하기 위해서 쌓임 맥락 계층을 그려보자.
- 루트 엘리먼트 쌓임 맥락
- DIV #2 (z-index 2)
- DIV #3 (z-index 1)
- DIV #4 (z-index 10)
Note: 일반적인 HTML 계층 구조가 쌓임 맥락 계층 구조와 다르다는걸 상기하자. 쌓임 맥락을 만들지 않는 엘리먼트들은 쌓임 맥락 계층 구조에서 사라진다.
예제 소스 코드
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
"https://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html>
<head><style type="text/css">
div { font: 12px Arial; }
span.bold { font-weight: bold; }
#div2 { z-index: 2; }
#div3 { z-index: 1; }
#div4 { z-index: 10; }
#div1,#div3 {
height: 80px;
position: relative;
border: 1px dashed #669966;
background-color: #ccffcc;
padding-left: 5px;
}
#div2 {
opacity: 0.8;
position: absolute;
width: 150px;
height: 200px;
top: 20px;
left: 170px;
border: 1px dashed #990000;
background-color: #ffdddd;
text-align: center;
}
#div4 {
opacity: 0.8;
position: absolute;
width: 200px;
height: 70px;
top: 65px;
left: 50px;
border: 1px dashed #000099;
background-color: #ddddff;
text-align: left;
padding-left: 10px;
}
</style></head>
<body>
<br />
<div id="div1">
<br /><span class="bold">DIV #1</span>
<br />position: relative;
<div id="div2">
<br /><span class="bold">DIV #2</span>
<br />position: absolute;
<br />z-index: 2;
</div>
</div>
<br />
<div id="div3">
<br /><span class="bold">DIV #3</span>
<br />position: relative;
<br />z-index: 1;
<div id="div4">
<br /><span class="bold">DIV #4</span>
<br />position: absolute;
<br />z-index: 10;
</div>
</div>
</body></html>
See also
- Stacking without z-index : Default stacking rules
- Stacking and float : How floating elements are handled
- Adding z-index : Using z-index to change default stacking
- The stacking context : Notes on the stacking context
- Stacking context example 1 : 2-level HTML hierarchy, z-index on the last level
- Stacking context example 3 : 3-level HTML hierarchy, z-index on the second level
Original Document Information
- Author(s): Paolo Lombardi
- This article is the english translation of an article I wrote in italian for YappY. I grant the right to share all the content under Creative Commons: Attribution-Sharealike license
- Last Updated Date: July 9th, 2005