我們的志工尚未將此文章翻譯為 正體中文 (繁體) 版本。加入我們,幫忙翻譯!
The mouseenter event is fired when a pointing device (usually a mouse) is moved over the element that has the listener attached.
Similar to mouseover, it differs in that it doesn't bubble and that it isn't sent when the pointer is moved from one of its descendants' physical space to its own physical space.
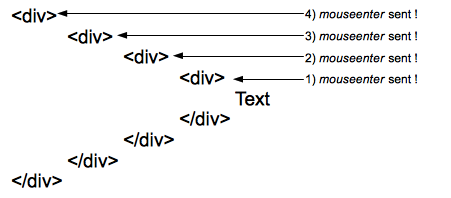
mouseenter event is sent to each element of the hierarchy when entering them. Here 4 events are sent to the four elements of the hierarchy when the pointer reaches the text.
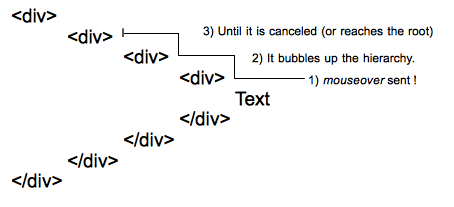
mouseover event is sent to the deepest element of the DOM tree, then it bubbles up the hierarchy until it is canceled by a handler or reaches the root.With deep hierarchies, the amount of mouseenter events sent can be quite huge and cause significant performance problems. In such cases, it is better to listen for mouseover events.
Combined with the behavior of its symmetrical event, mouseleave, the mouseenter DOM Event acts in a very similar way to the CSS :hover pseudo-class.
General info
- Specification
- DOM L3
- Interface
MouseEvent- Synchronicity
- Synchronous
- Bubbles
- No
- Cancelable
- No
- Target
- Element
- Default Action
- None
Properties
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
target Read only |
EventTarget |
The event target (the topmost target in the DOM tree). |
type Read only |
DOMString |
The type of event. |
bubbles Read only |
Boolean |
Whether the event normally bubbles or not |
cancelable Read only |
Boolean |
Whether the event is cancellable or not? |
view Read only |
WindowProxy |
document.defaultView (window of the document) |
detail Read only |
long (float) |
0. |
currentTarget Read only |
EventTarget | The node that had the event listener attached. |
relatedTarget Read only |
EventTarget | For mouseover, mouseout, mouseenter and mouseleave events: the target of the complementary event (the mouseleave target in the case of a mouseenter event). null otherwise. |
screenX Read only |
long | The X coordinate of the mouse pointer in global (screen) coordinates. |
screenY Read only |
long | The Y coordinate of the mouse pointer in global (screen) coordinates. |
clientX Read only |
long | The X coordinate of the mouse pointer in local (DOM content) coordinates. |
clientY Read only |
long | The Y coordinate of the mouse pointer in local (DOM content) coordinates. |
button Read only |
unsigned short | The button number that was pressed when the mouse event was fired: Left button=0, middle button=1 (if present), right button=2. For mice configured for left handed use in which the button actions are reversed the values are instead read from right to left. |
buttons Read only |
unsigned short | The buttons being pressed when the mouse event was fired: Left button=1, Right button=2, Middle (wheel) button=4, 4th button (typically, "Browser Back" button)=8, 5th button (typically, "Browser Forward" button)=16. If two or more buttons are pressed, returns the logical sum of the values. E.g., if Left button and Right button are pressed, returns 3 (=1 | 2). More info. |
mozPressure Read only |
float | The amount of pressure applied to a touch or tabdevice when generating the event; this value ranges between 0.0 (minimum pressure) and 1.0 (maximum pressure). |
Examples
The mouseover documentation has an example illustrating the difference between mouseover and mouseenter.
The following example illustrates how to use mouseover to simulate the principle of event delegation for the mouseenter event.
<ul id="test">
<li>
<ul class="enter-sensitive">
<li>item 1-1</li>
<li>item 1-2</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>
<ul class="enter-sensitive">
<li>item 2-1</li>
<li>item 2-2</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
<script>
var delegationSelector = ".enter-sensitive";
document.getElementById("test").addEventListener("mouseover", function( event ) {
var target = event.target,
related = event.relatedTarget,
match;
// search for a parent node matching the delegation selector
while ( target && target != document && !( match = matches( target, delegationSelector ) ) ) {
target = target.parentNode;
}
// exit if no matching node has been found
if ( !match ) { return; }
// loop through the parent of the related target to make sure that it's not a child of the target
while ( related && related != target && related != document ) {
related = related.parentNode;
}
// exit if this is the case
if ( related == target ) { return; }
// the "delegated mouseenter" handler can now be executed
// change the color of the text
target.style.color = "orange";
// reset the color after a small amount of time
setTimeout(function() {
target.style.color = "";
}, 500);
}, false);
// function used to check if a DOM element matches a given selector
// the following code can be replaced by this IE8 compatible function: https://gist.github.com/2851541
function matches( elem, selector ){
// the matchesSelector is prefixed in most (if not all) browsers
return elem.matchesSelector( selector );
};
</script>
Browser compatibility
| Feature | Chrome | Firefox (Gecko) | Internet Explorer | Opera | Safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic support | 30[1] | 10[2] | 5.5 | (Yes) Not supported 15.0 17.0 |
7[3] |
| On disabled form elements | Not supported | 44.0 (44.0)[4] | Not supported | Not supported | ? |
| Feature | Android | Chrome for Android | Firefox Mobile (Gecko) | IE Mobile | Opera Mobile | Safari Mobile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic support | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| On disabled form elements | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? |
[1] Implemented in bug 236215.
[2] Implemented in bug 432698.
[3] Safari 7 fires the event in many situations where it's not allowed to, making the whole event useless. See bug 470258 for the description of the bug (it existed in old Chrome versions as well). Safari 8 has correct behavior
[4] Implemented in bug 218093.