Deze vertaling is niet volledig. Help dit artikel te vertalen vanuit het Engels.
Wanneer een gebruiker een pagina bezoekt die via HTTPS wordt verzonden, wordt de verbinding beveliligd door middel van SSL om afluisteren te voorkomen.
Mocht de bekeken pagina elementen bevatten die worden opgehaald via reguliere HTTP, is de verbinding slechts gedeeltelijk beveiligd. Deze onbeveiligde inhoud is wel kwetsbaar voor man-in-the-middle aanvallen en afluisteren.
Wanneer een pagina een dergelijk gedrag vertoont, wordt dit een mixed content (gemendge inhoud) pagina genoemd.
Web Console
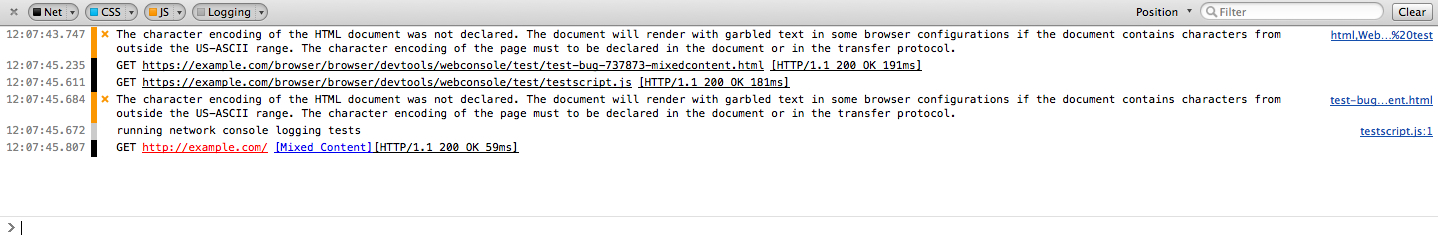
Vanaf Firefox 16, wordt in de Web Console een waarschuwing getoond indien de pagina dit probleem bevat. Het onderdeel dat over HTTP wordt opgehaald wordt in het rood getoond, samen met de text "mixed content" en een link naar deze pagina.
Om dit probleem te verhelpen, moeten alle aanvragen over HTTP worden vervangen door aanvragen die HTTPS gebruiken. In veel gevallen gaat het hier over JavaScript bestanden, stylesheets, afbeeldingen, videos en andere media.
Vanaf Firefox 23 wordt mixed content standaard geblokkerd (en kan ook via een instelling worden geblokkeerd). Om het makkelijker te maken voor ontwikkelaars om mixed content fouten te vinden, worden alle geblokkeerde mixed content aanvragen getoond in het Security pneel van de Web Console.
Types of Mixed Content
There are two categories for mixed content: Mixed Passive/Display Content and Mixed Active Content. The difference lies in the threat level of the worst case scenario if content is rewritten as part of a Man-In-The-Middle attack. In the case of passive content, the threat is low (webpage appears broken or with misleading content). In the case of active content, the threat can lead to phishing, sensitive data disclosure, redirection to malicious sites, etc.
Mixed passive/display content
Mixed Passive/Display Content is content served over HTTP that is included in an HTTPS webpage, but that cannot alter other portions of the webpage. For example, an attacker could replace an image served over HTTP with an inappropriate image or message to the user. The attacker could also infer information about the user's activities by watching which images are served to the user; often images are only served on a specific page within a website. If the attacker observes HTTP requests to certain images, he could determine which webpage the user is visiting.
Passive content list
This section lists all types of HTTP requests which are considered passive content:
- <audio> (
srcattribute) - <img> (
srcattribute) - <video> (
srcattribute) - <object> subresources (when an <object> performs HTTP requests)
Mixed active content
Mixed Active Content is content that has access to all or parts of the Document Object Model of the HTTPS page. This type of mixed content can alter the behavior of the HTTPS page and potentially steal sensitive data from the user. Hence, in addition to the risks described for Mixed Display Content above, Mixed Active Content is vulnerable to a few other attack vectors.
In the Mixed Active Content case, a man-in-the-middle attacker can intercept the request for the HTTP content. The attacker can also rewrite the response to include malicious JavaScript code. Malicious active content can steal the user's credentials, acquire sensitive data about the user, or attempt to install malware on the user's system (by leveraging vulnerabilities in the browser or its plugins, for example).
The risk involved with mixed content does depend on the type of website the user is visiting and how sensitive the data exposed to that site may be. The webpage may have public data visible to the world or private data visible only when authenticated. If the webpage is public and has no sensitive data about the user, using Mixed Active Content still provides the attacker with the opportunity to redirect the user to other HTTP pages and steal HTTP cookies from those sites.
Active content list
This section lists some types of HTTP requests which are considered active content:
- <script> (
srcattribute) - <link> (
hrefattribute) (this includes CSS stylesheets) - XMLHttpRequest object requests
- <iframe> (
srcattributes) - All cases in CSS where a url value is used (@font-face, cursor, background-image, etc.)
- <object> (
dataattribute)
See also