« CSS « UNDERSTANDING CSS Z-INDEX
Stacking without z-index
When no element has z-index, the elements are stacked in this order (from the bottom to the top):
- Background and borders of the root element
- Descendant blocks in the normal flow, in appearance order (in HTML)
- Descendant elements by position, in appearance order (in HTML)
En the following example, the blocks with absolute and relative positions are properly sized and positioned to illustrate the stacking rules.
Notes:
- Given homogeneous group of elements with no z-index property, such as the posiitoned blocks (DIV #1 to #4) in the example, the stacking order of the elements is its order in the HTML hierarchy, regardless its position.
-
Standar blocks (DIV #5) in the normal flow, with no position property, are always redered before the positioned elements and appear below of them, even if they come later in the HTML hierarchy.
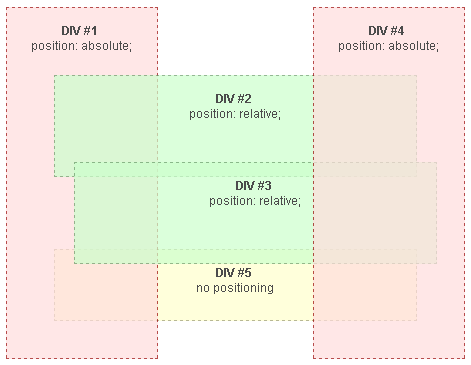
Example
HTML
<div id="absdiv1"> <br /><span class="bold">DIV #1</span> <br />position: absolute; </div> <div id="reldiv1"> <br /><span class="bold">DIV #2</span> <br />position: relative; </div> <div id="reldiv2"> <br /><span class="bold">DIV #3</span> <br />position: relative; </div> <div id="absdiv2"> <br /><span class="bold">DIV #4</span> <br />position: absolute; </div> <div id="normdiv"> <br /><span class="bold">DIV #5</span> <br />no positioning </div>
CSS
.bold {
font-weight: bold;
font: 12px Arial;
}
#normdiv {
height: 70px;
border: 1px dashed #999966;
background-color: #ffffcc;
margin: 0px 50px 0px 50px;
text-align: center;
}
#reldiv1 {
opacity: 0.7;
height: 100px;
position: relative;
top: 30px;
border: 1px dashed #669966;
background-color: #ccffcc;
margin: 0px 50px 0px 50px;
text-align: center;
}
#reldiv2 {
opacity: 0.7;
height: 100px;
position: relative;
top: 15px;
left: 20px;
border: 1px dashed #669966;
background-color: #ccffcc;
margin: 0px 50px 0px 50px;
text-align: center;
}
#absdiv1 {
opacity: 0.7;
position: absolute;
width: 150px;
height: 350px;
top: 10px;
left: 10px;
border: 1px dashed #990000;
background-color: #ffdddd;
text-align: center;
}
#absdiv2 {
opacity: 0.7;
position: absolute;
width: 150px;
height: 350px;
top: 10px;
right: 10px;
border: 1px dashed #990000;
background-color: #ffdddd;
text-align: center;
}
Result
(If the image doesn't appear in CodePen, click in the Tidy button from the CSS section)
{{ EmbedLiveSample('Example', '', '', '', 'Web/CSS/CSS_Positioning/Understanding_z_index/Stacking_without_z-index') }}
See also
- Stacking and float : How floating elements are handled
- Adding z-index : Using z-index to change default stacking
- The stacking context : Notes on the stacking context
- Stacking context example 1 : 2-level HTML hierarchy, z-index on the last level
- Stacking context example 2 : 2-level HTML hierarchy, z-index on all levels
- Stacking context example 3 : 3-level HTML hierarchy, z-index on the second level
Original Document Information
- Author(s): Paolo Lombardi
- This article is the english translation of an article I wrote in italian for YappY. I grant the right to share all the content under Creative Commons: Attribution-Sharealike license
- Last Updated Date: November 3rd, 2014